Cell | Nanoparticles Hijack Brain Immune Cells for Central Nervous System Drug Delivery and Stroke Therapy
QQ Academic Group: 1092348845
Detailed
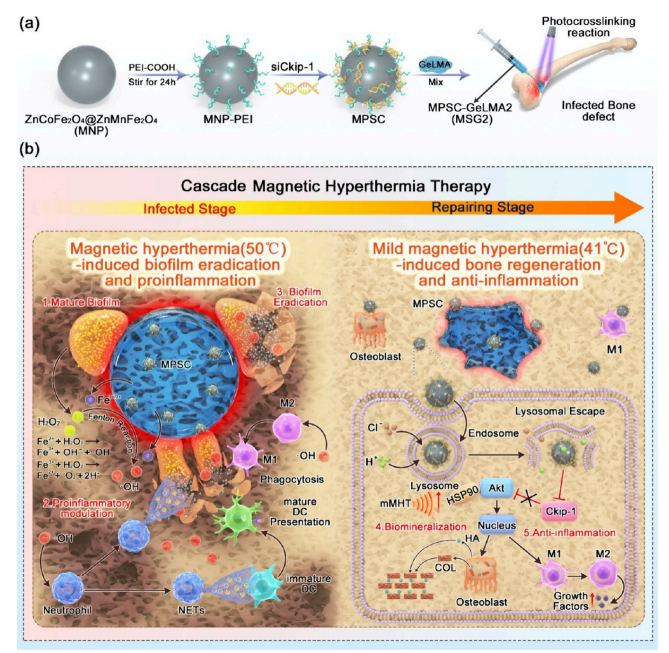
Infectious bone defect (IBD) treatment presents significant challenges in current orthopedics due to the complexity of these defects, as well as the diverse needs involving infection control and subsequent bone regeneration. Current available treatments often fail to effectively address these multifaceted needs. Herein, we propose a cascade magnetic hyperthermia (cMHT) strategy using MNP-PEI-siCkip-1 (MPSC), a magnetogenic nanoplatform constructed by siRNAs coated with casein kinase-2 interacting protein-1 (siCkip-1) and polyethyleneimide-carboxylic acid (PEI-COOH) on ZnCoFe2O4@ZnMnFe2O4 nanoparticles. These MPSCs are then embedded in gelatin methacrylyl (GelMA) to form nanocatalytic nanoparticle-hydrogel complexes (MSGs) that exhibit strong magnetothermal effects. During disinfection, MSG hydrogels generate MHT (∼50 °C) under an alternative magnetic field (AMF) to disrupt dense biofilms and catalyze the production of hydroxyl radicals (•OH) in the biofilm microenvironment (BME) to fight infection. • Increased OH production also promotes pro-inflammatory modulation of innate immunity to eradicate bacteria. After resolution of the infection, AMF is adjusted to induce mild MHT (∼41 °C, mMHT) to promote osteogenesis and inhibit excessive inflammation. Gradual MSG hydrogel down-release MPSCs deliver siCkip-1 with osteogenic and anti-inflammatory activity to osteoblasts and macrophages. This cascade magnetic hyperthermia (cMHT) strategy offers a compelling solution to the multifaceted challenges of IBD treatment, addressing critical aspects such as infection control and bone regeneration. This innovative approach underscores the potential of cMHT as a transformative treatment option for IBD, potentially leading to improved treatment outcomes.
 For the orthopedic clinical problem of infectious bone defects (IBDs), traditional therapies often struggle to balance the dual needs of anti-infection and bone regeneration. Recently, a study published in ACS Nano proposed an innovative cascade magnetic thermotherapy (cMHT) strategy to provide a new solution for the comprehensive treatment of IBDs by constructing a multifunctional magnetogenetic nanoplatform.
For the orthopedic clinical problem of infectious bone defects (IBDs), traditional therapies often struggle to balance the dual needs of anti-infection and bone regeneration. Recently, a study published in ACS Nano proposed an innovative cascade magnetic thermotherapy (cMHT) strategy to provide a new solution for the comprehensive treatment of IBDs by constructing a multifunctional magnetogenetic nanoplatform.
 Reference News:
Reference News:
return
- Previous: Advanced Materials | G
- Next: ACS Nano | Materials I

 mxene academic
mxene academic