AFM: Polysiloxane Crosslinked Stabilized MXene-Based Lithium Host for Ultrastable Lithium Metal Anode
QQ Academic Group: 1092348845
Detailed
In the beginning of the school season, Beikenami MXene and other materials will start a 10% discount event, the number is limited, come and participate!


Research Background
To meet the requirements of practical energy storage applications, it is necessary to develop secondary batteries with high energy/power density and long charge-discharge life. Although lithium (Li)-ion batteries have been commercialized since 1991, the energy density of graphite-anode Li-ion batteries is close to its theoretical limit of 372 mAh g−1, which cannot meet the high energy demands of emerging applications.
Introduction
Recently, the research group of Professor Jiajie Liang of Nankai University published a research paper titled Polysiloxane Cross-Linked Mechanically Stable MXene-Based Lithium Host for Ultrastable Lithium Metal Anodes with Ultrahigh Current Densities and Capacities in the internationally renowned academic journal Advanced Functional Materials.
Graphical guide
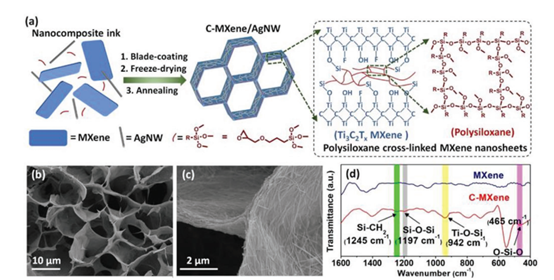
Figure 1. a) Synthesis schematic diagram of C-MXene/AgNW scaffold b) C-MXene/AgNW framework cross section c) C-MXene/AgNW framework magnification d) C-MXene/AgNW scaffold IR spectrum.
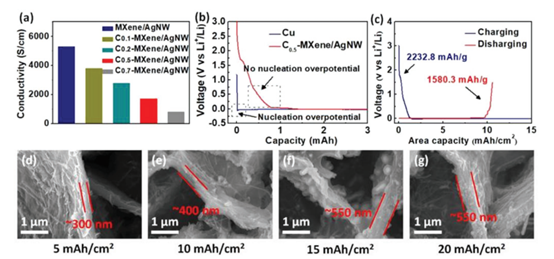
Figure 2. C-MXene/AgNW conductivity and lithium intercalation characterization.
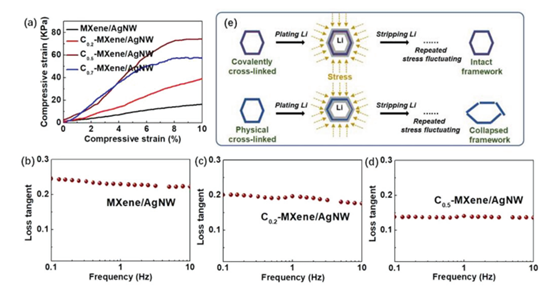
Figure 3. Mechanical properties of C-MXene/AgNW frameworks.
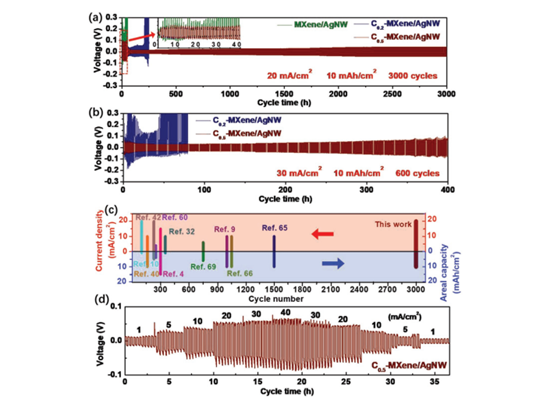
Figure 4. Cycling performance of C-MXene/AgNW framework.
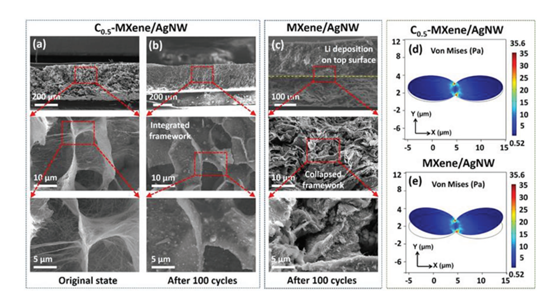
Figure 5. Changes and simulations of C-MXene/AgNW before and after cycling.
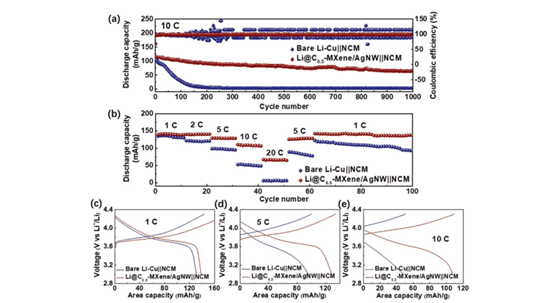
Figure 6. Li metal full cell test based on C-MXene/AgNW.
Summary of this article
The strategy of this study focuses on optimizing the mechanical stability of the lithium metal host, an important but widely overlooked property, to significantly improve the cycle life of lithium metal anodes. Conductive MXene/AgNW scaffolds were fabricated through the weak van der Waals force that caused the scaffold to collapse due to large stress fluctuations during Li coating peeling.

- Previous: JCIS: N/S co-doped V-b
- Next: Advanced Materials | A

 mxene academic
mxene academic