已传文件:photo/1769650043.png
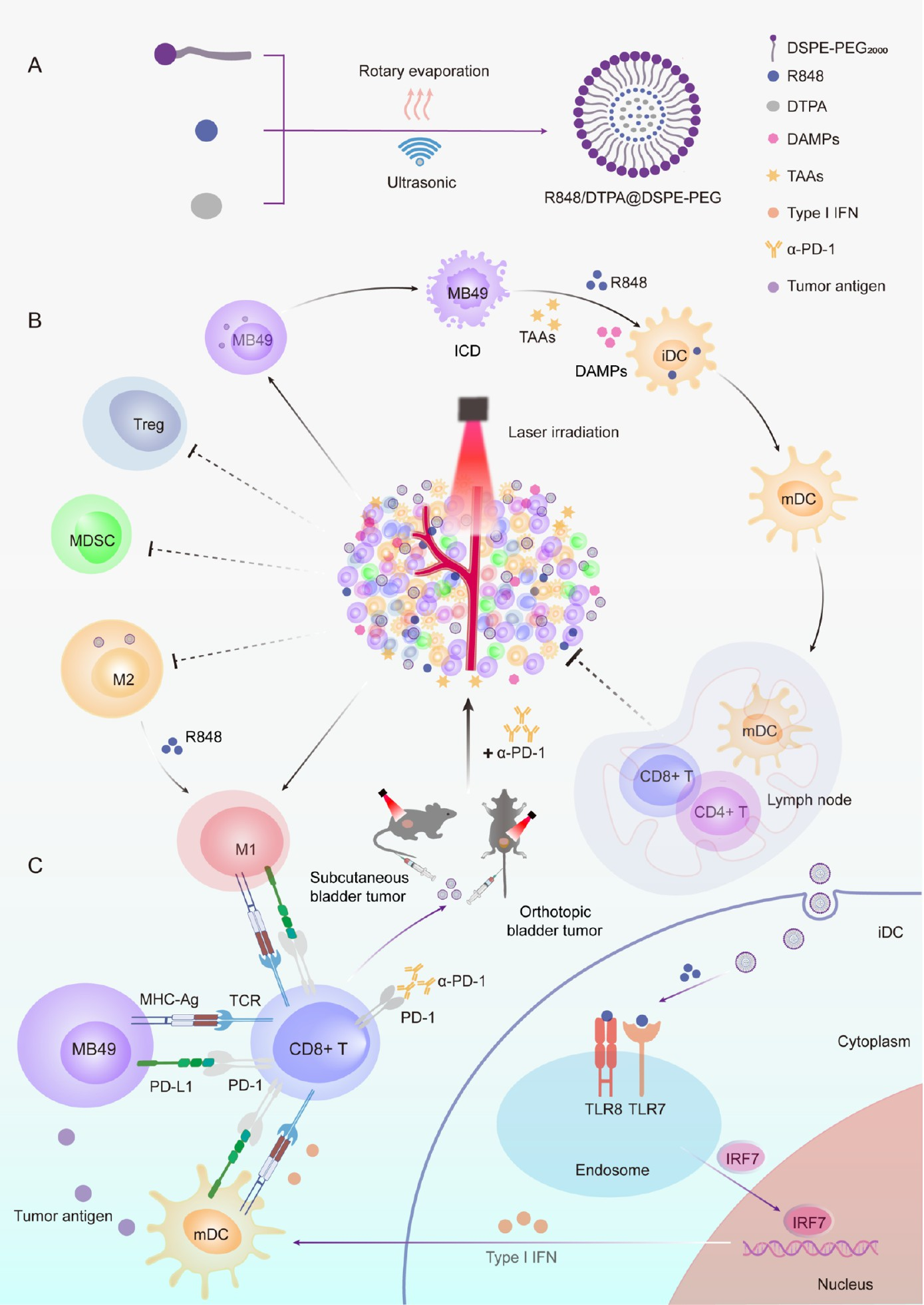
Bladder cancer is a common malignant tumor of the urinary system and is associated with high incidence, recurrence, and mortality rates. Immunotherapy using immune checkpoint inhibitors has shown good therapeutic effects and safety in bladder cancer. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have also been approved as first- and second-line treatments for locally advanced or metastatic bladder cancer. However, immunotherapy has a relatively low response and adjuvant effect in cancer immunotherapy, which may be attributed to insufficient antigen presentation in the tumor microenvironment, accumulation of immunosuppressive cells, and T lymphocyte exhaustion.To overcome the limitations of immunotherapy, we prepared lipid nanoparticles loaded with R848 (resiquimod) and a photothermal agent (DTPA) (R848/DTPA@DSPE-PEG NPs), which exhibited good photothermal conversion efficiency, biocompatibility, and biosafety. R848/DTPA@DSPE-PEG NPs irradiated with a 635 nm laser can damage MB49 cells and induce immunogenic cell death in vitro, thereby triggering an immune response. Additionally, R848/DTPA@DSPE-PEG NPs can promote M1-like macrophage polarization and dendritic cell maturation in vitro.In addition, R848/DTPA@DSPE-PEG NPs, under 635 nm laser irradiation, can inhibit the growth of subcutaneous and orthotopic bladder tumors while activating immune responses. They promote dendritic cell maturation and M1-like macrophage polarization, enhance CD8 T lymphocyte infiltration, and reduce M2-like macrophage polarization in tumors. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that R848/DTPA@DSPE-PEG NPs can also induce overexpression of immune-related genes in immune signaling pathways. When combined with PD-1 antibodies, R848/DTPA@DSPE-PEG NPs can significantly enhance antitumor therapeutic effects, reprogram the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment, and prolong survival.

This study reports a novel thermosensitive R848-loaded lipid nanoparticle (R848/DTPA@DSPE-PEG NPs), designed to enhance the therapeutic effect of bladder cancer through photothermal-immunotherapy combination. Bladder cancer, as a highly prevalent, recurrent, and fatal malignancy of the urinary system, has shown some response to traditional immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy, but its response rate is relatively low and often limited by the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment. This study effectively overcomes the limitations of monotherapy by synthesizing nanoparticles that possess both photothermal conversion capability and immunoadjuvant function, providing an innovative strategy for bladder cancer immunotherapy.
Reference News:
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c17444





