IF 16! Nanozyme-coated macrophage mitochondrial metabolism reprogramming for immunomodulation and bone integration in rheumatoid arthritis cases
QQ Academic Group: 1092348845
Detailed
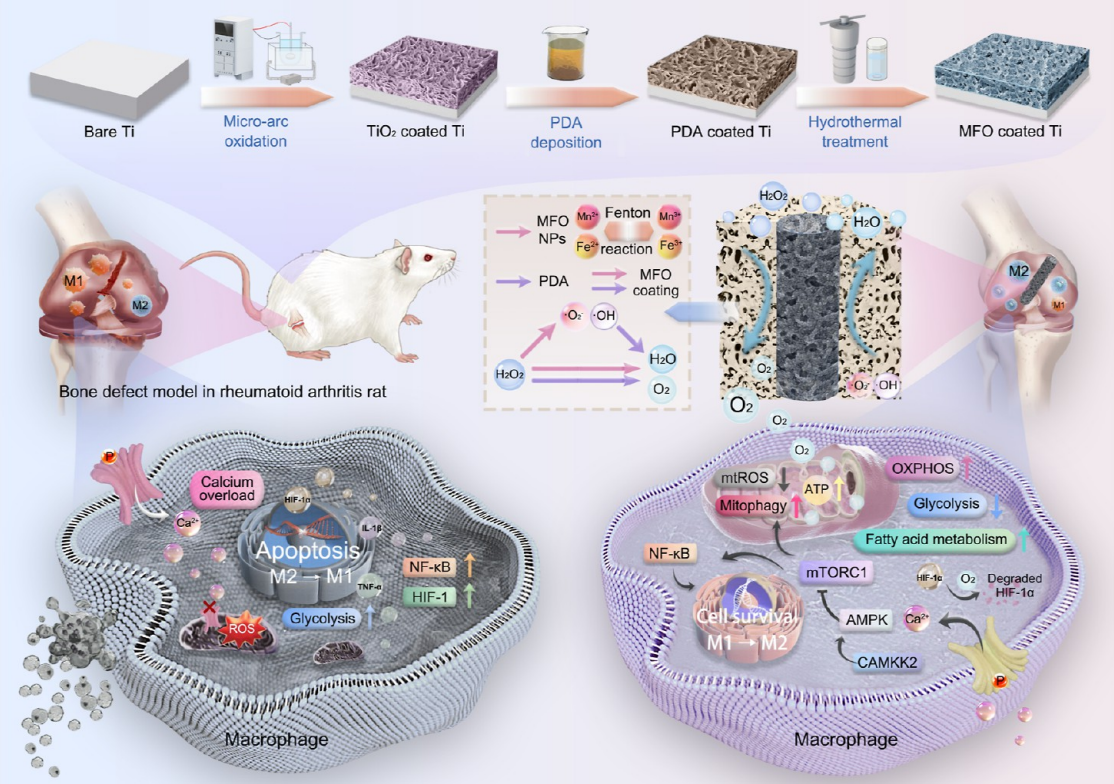
Traditional titanium-based implants are prone to mitochondrial damage and M1 polarization of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) bone defects due to a high ROS and hypoxic microenvironment, which hinders bone integration. Researchers have constructed a MnFe₂O₄ nanozyme coating (MFO coating) on the surface of titanium, leveraging its ability to efficiently convert H₂O₂ into O₂ and scavenge ROS.Reduces mitochondrial ROS accumulation and Ca²⁺ overload, maintains O₂ levels to prevent cell apoptosis; activates mitophagy through the Ca²⁺-AMPK-mTOR pathway, restores mitochondrial function, promotes a switch to oxidative phosphorylation, drives macrophage M2 polarization, inhibits osteoclast activity, and accelerates bone integration. This coating provides a new strategy for the design of implants for inflammatory bone defects, with the potential to reduce revision risks and extend service life.
 Original link
Original link
Nanozyme Coating-Mediated Mitochondrial Metabolic Reprogramming of Macrophages for Immunomodulatory
Osseointegration in Rheumatoid Arthritis Case
Pub Date : 2025-07-08
DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.5c07535
Shimeng Chen, Xiaoqi Liu, Wenhui Zhang, Bo Li, Fuwei Liu, Yingang Zhang, Yong Han
ACS Nano ( IF 16 )
- Previous: IF 26.8! Immunomodulat
- Next: 没有了...

 Academic Frontier
Academic Frontier